How Improved Airflow Contributes to Enhanced Indoor Air Quality
The Importance of Airflow in Indoor Spaces
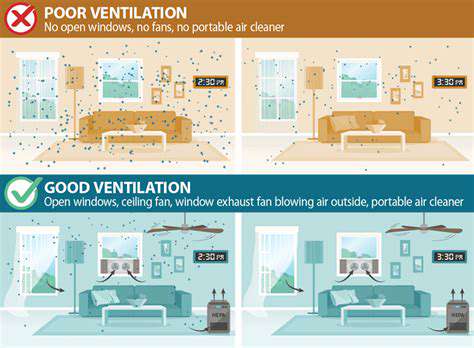
The Role of Airflow in Diluting Indoor Pollutants
Indoor spaces can accumulate various pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), dust, and allergens over time. Improved airflow helps to dilute these pollutants, reducing their concentration in the air. This is especially crucial in environments such as offices, schools, and homes where people spend a significant amount of time.
Proper airflow allows fresh outdoor air to enter and circulate within indoor spaces. This exchange of air minimizes the stale air that can lead to health issues, ensuring a healthier living or working environment. Additionally, adequate airflow helps maintain humidity levels, thus preventing mold growth.
Natural ventilation and mechanical systems play a vital role in facilitating this airflow. By designing buildings with optimal airflow considerations, architects and builders contribute to the overall well-being of occupants. Regular maintenance of air handling systems is also essential to keep airflow at its best.
Ultimately, improving indoor airflow is not just about comfort; it directly impacts cognitive function and productivity. Ensuring good airflow can lead to higher energy levels and improved focus among individuals. Thus, enhancing indoor air quality through effective airflow management is a fundamental aspect of healthy living spaces.
Strategies for Optimizing Indoor Airflow
To achieve optimal indoor airflow, several strategies can be employed. One effective method is to utilize cross-ventilation, which involves using windows and vents on opposite sides of a room to create a natural breeze. This approach effectively enhances fresh air intake and promotes circulation.
Another key strategy is to ensure that air filters and purification systems are routinely inspected and replaced. Clean filters enhance airflow efficiency, while air purifiers help filter out harmful particulates. Regular maintenance ensures that these systems operate effectively and contribute to improved indoor air quality.
Moreover, the layout of furniture and other obstacles should be taken into account. Arranging furniture to avoid blocking vents and pathways can significantly improve air circulation within a room. Additionally, utilizing ceiling fans can help to distribute air evenly throughout a space.
Finally, incorporating plants into indoor environments can offer natural air purification benefits. Many houseplants are known to remove toxins from the air while adding moisture, which further contributes to a comfortable environment. By applying these strategies, individuals can create healthier indoor spaces with optimal airflow.
How Improved Airflow Enhances Indoor Air Quality

Understanding Indoor Air Quality
Indoor air quality (IAQ) refers to the condition of the air inside buildings and structures, particularly as it relates to the health and comfort of the occupants. Factors that influence IAQ include pollutants, humidity, temperature, and airflow. Maintaining high levels of IAQ is crucial as it can significantly affect physical health, productivity, and overall well-being.
Common indoor air pollutants include allergens, dust, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Regular monitoring of these components is essential for ensuring a healthy living and working environment.
The Role of Airflow in Pollutant Management
Airflow is a major factor in how indoor pollutants are dispersed and diluted. Improved airflow helps in the efficient removal of contaminants, thereby enhancing the overall air quality in a space. By facilitating a steady flow of fresh air, we can significantly reduce the concentration of harmful particles.
Proper airflow helps to minimize the stagnation of air, which can trap pollutants, leading to health issues among occupants. This is particularly important in spaces with high occupancy or activities that generate pollutants, such as cooking or cleaning.
Benefits of Enhanced Airflow Systems
Upgraded airflow systems can lead to improved ventilation, which naturally bolsters indoor air quality. These systems often incorporate advanced filtration technologies that capture a higher percentage of airborne contaminants. Such systems not only enhance comfort but also promote a healthier living environment.
Incorporating features like variable speed fans and programmable thermostats can optimize airflow based on real-time needs, ensuring an efficient and responsive environment. This dynamic adjustment can prevent both over-ventilation and under-ventilation situations.
Impact of Humidity Control on Air Quality
Humidity plays a significant role in indoor air quality, influencing both comfort and health. Too much moisture can encourage mold growth and dust mites, while too little can lead to dry skin and respiratory issues. Effective airflow management helps regulate humidity levels, contributing to better air quality.
Dehumidifiers and humidifiers can be integrated into the ventilation system to achieve optimal humidity levels. This balance is vital for preventing respiratory problems and ensuring a comfortable indoor environment.
Best Practices for Improving Airflow
To achieve better airflow, regular maintenance of HVAC systems is crucial. Filters should be replaced frequently, and ducts should be cleaned to prevent blockages and ensure optimal air movement throughout the space. Strategic placement of vents and the use of ceiling fans can also enhance airflow efficiency.
Additionally, residents and building managers should assess the layout of furniture and decor to avoid obstructing air entry points. Creating an open and breathable environment is essential for maximizing airflow and ensuring a continuously fresh indoor atmosphere.
Strategies for Improving Airflow in Indoor Spaces
Benefits of Improved Airflow
Improved airflow is crucial in maintaining good indoor air quality. It helps to remove stale air and replace it with fresh air, reducing the concentration of pollutants and allergens. This can lead to a healthier environment, especially for people with respiratory issues. Additionally, improved airflow can help to reduce the risk of mold growth and the spread of airborne diseases.
Furthermore, improved airflow can also contribute to increased productivity and comfort in indoor spaces. When the air is fresh and clean, people are more likely to feel energized and focused, leading to better work performance and overall well-being.
Strategies for Enhancing Airflow in Indoor Spaces
There are several strategies that can be employed to enhance airflow in indoor spaces. One of the most effective methods is to install ventilation systems that can bring in fresh air from outside and remove stale air from the building. This can be achieved through the use of whole-house fans, heat recovery ventilation systems, or energy recovery ventilation systems.
Another strategy is to improve the layout of the space to promote better airflow. This can be done by creating a path for air to circulate through the space, such as by placing furniture away from walls or creating a breezeway between rooms. Additionally, using vertical elements such as floor-to-ceiling curtains or screens can help to direct airflow and reduce the risk of stagnation.



