Maximize Your Productivity with the Eisenhower Matrix: A Comprehensive Guide
How the Eisenhower Matrix Works
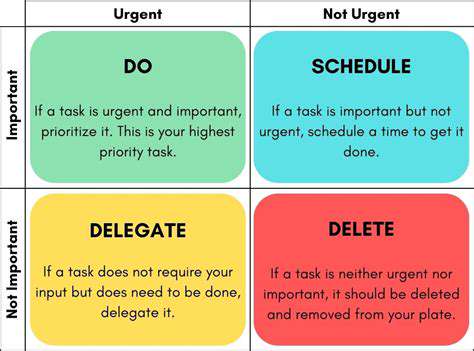
Understanding the Four Quadrants
The Eisenhower Matrix is divided into four distinct quadrants, each designed to help users categorize their tasks based on urgency and importance. Quadrant I is for tasks that are both urgent and important, which require immediate attention. These are typically deadlines or crises that cannot be ignored. Identifying these tasks ensures that you handle them promptly, reducing stress and improving overall efficiency.
Quadrant II consists of tasks that are important but not urgent. These tasks often include long-term goals, professional development, and relationship-building activities. While they may not require immediate action, neglecting them can lead to increased urgency later on. Regularly investing time in Quadrant II can enhance personal and professional growth.
Quadrant III encompasses tasks that are urgent but not important. These tasks often involve other people’s priorities and can distract you from your goals. Learning to delegate or say no to these tasks is crucial for maintaining focus on what truly matters. By minimizing time spent on Quadrant III tasks, you can allocate more energy to the important ones.
Finally, Quadrant IV covers tasks that are neither urgent nor important. These activities can be time-wasters, often characterized by distractions like social media or excessive television. Recognizing and limiting these tasks can free up valuable time that can be redirected towards more productive pursuits.
Implementing the Matrix in Daily Life
To effectively use the Eisenhower Matrix, start by listing all your current tasks and responsibilities. Once you have a comprehensive list, evaluate each task according to the criteria of urgency and importance. This initial assessment is crucial in effectively organizing your workload. The clarity gained from categorizing tasks can significantly alleviate feelings of overwhelm.
Create a visual representation of the matrix to keep your priorities front and center. You can draw it on paper, use a digital app, or even a simple spreadsheet. Having a visual aid facilitates quicker decision-making and can serve as a daily reminder to focus on what truly matters as you progress through your day.
Incorporating weekly reviews into your routine is also beneficial. Take time to reflect on what tasks fell into each quadrant over the past week and assess how you can improve your task management moving forward. This reflection not only ensures that you remain on track but also builds a routine that encourages continuous improvement and productivity.
Common Challenges and Solutions
One of the main challenges users encounter when implementing the Eisenhower Matrix is the difficulty in categorizing tasks accurately. Sometimes, a task may seem urgent at first glance but might not hold long-term importance. To overcome this, consider consulting with a colleague or mentor for a second opinion to gain perspective and clarify priorities.
Another challenge is the tendency to become overwhelmed by Quadrant I tasks, which can lead to burnout. It's essential to break larger tasks into manageable steps and set realistic deadlines. Additionally, taking regular breaks can enhance productivity and keep energy levels high, ultimately allowing for better focus on important tasks.
Finally, individuals may struggle with saying no to tasks that fall into Quadrant III. This is often due to a desire to help others or a fear of disappointing colleagues. Learning to recognize your limits and communicating them effectively can help you maintain control over your time management. Practice assertiveness in your responses to these requests, ensuring that you prioritize your own responsibilities.
The Long-term Benefits of Using the Matrix
Utilizing the Eisenhower Matrix regularly can lead to significant long-term benefits in your personal and professional life. By consistently focusing on what's important, individuals often report higher levels of productivity, better time management, and improved clarity about their goals. This structured approach to prioritization fosters a proactive mindset that can transform how you handle daily demands.
Additionally, adhering to the matrix can enhance decision-making skills over time. As you become accustomed to evaluating tasks based on urgency and importance, you'll develop a sharper intuition for distinguishing between what truly deserves your attention and what can be deferred or delegated.
Finally, the increased organization and prioritization that comes from using the Eisenhower Matrix can reduce stress and improve overall well-being. Individuals who effectively manage their time are likely to experience a better work-life balance, allowing for more time to invest in personal interests and relationships. Ultimately, this holistic approach fosters a lifestyle that promotes not only productivity but also overall happiness and fulfillment.
Steps to Implement the Eisenhower Matrix
Understanding the Eisenhower Matrix
The Eisenhower Matrix is a simple yet effective tool that helps individuals prioritize tasks based on their urgency and importance. By categorizing tasks into four distinct quadrants, you can make informed decisions about where to focus your efforts.
This method was named after President Dwight D. Eisenhower, who famously stated, “What is important is seldom urgent and what is urgent is seldom important.” This philosophy underlies the matrix's premise, emphasizing the need to differentiate between urgent tasks and those that truly matter.
Setting Up Your Quadrants
The matrix consists of four quadrants: Quadrant 1 contains urgent and important tasks, Quadrant 2 includes important but not urgent tasks, Quadrant 3 has urgent but not important tasks, and Quadrant 4 consists of neither urgent nor important tasks. Properly categorizing tasks into these quadrants is crucial for maximizing productivity.
To set up your matrix, create a simple grid and label each quadrant accordingly. As you list your tasks, evaluate them based on urgency and importance to ensure accurate placement.
Prioritizing Your Tasks Effectively
Once your tasks are categorized, it's time to prioritize them effectively. Begin with Quadrant 1, addressing urgent and important tasks first, as these require immediate attention and have significant consequences if neglected.
After completing these tasks, shift your focus to Quadrant 2. Allocating time for important but not urgent tasks is essential for long-term success. By managing these tasks proactively, you can prevent them from becoming urgent later on.
Reviewing and Adjusting Your Matrix
Regularly reviewing and adjusting your Eisenhower Matrix ensures that it remains relevant to your goals and commitments. New tasks may emerge, and priorities can shift, necessitating updates to the matrix structure.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
As you implement the Eisenhower Matrix, be mindful of common pitfalls that can hinder your productivity. One major mistake is failing to accurately assess the importance of tasks, resulting in misallocation within the quadrants.
Additionally, many individuals tend to spend too much time on Quadrant 3 tasks, those that are urgent but not important. By recognizing this tendency and consciously shifting focus to more impactful tasks, you can enhance your overall efficiency.
Benefits of Using the Eisenhower Matrix

Improved Time Management
The Eisenhower Matrix offers a structured approach to time management by helping you prioritize tasks based on urgency and importance. This method allows you to focus on what truly matters, significantly reducing time spent on less critical activities.
By categorizing tasks into four quadrants, you can quickly identify areas that require your attention. This clarity leads to more efficient decision-making and enhances your overall productivity.
Enhanced Focus on Key Tasks
With the Eisenhower Matrix, you can concentrate your efforts on high-impact tasks that contribute to your long-term goals. This encourages a proactive mindset, enabling you to tackle important projects without succumbing to distractions.
When you prioritize effectively, you are less likely to feel overwhelmed by less significant tasks. Ultimately, this focus allows for deeper engagement in your work.
Reduction of Stress and Burnout
Implementing the Eisenhower Matrix can lead to a more manageable workload, which significantly reduces stress levels. By distinguishing between what is urgent and what is truly important, you can avoid last-minute rushes and the anxiety that comes with them.
Prioritizing effectively leads to a more organized workday, fostering a sense of accomplishment. This reduction in pressure helps prevent burnout, ensuring that you maintain a sustainable workflow.
Better Work-Life Balance
Using the Eisenhower Matrix allows for better separation between professional responsibilities and personal life. By identifying tasks that can be delegated or eliminated, you free up time to spend on activities that rejuvenate you outside of work.
This balance is crucial for long-term happiness and productivity. By ensuring that you make time for both your responsibilities and personal interests, you cultivate a more fulfilled life.
Increased Accountability and Goal Setting
The Eisenhower Matrix encourages accountability by requiring you to regularly assess your tasks and prioritize them accordingly. This practice promotes a goal-oriented approach, where each task is aligned with your broader objectives.
By regularly reviewing and adjusting your matrix, you can track your progress and stay committed to your goals. This fosters a greater sense of ownership over your work and leads to more meaningful outcomes.