Maximizing Performance and Fuel Economy with Turbocharged Engines
The Evolution and Mechanics of Turbocharged Engines
The Historical Development of Turbocharging
Turbocharging has a rich history that dates back to the early 20th century. The concept was first explored by engineer Alfred Buchi, who patented the turbocharger in 1905. His goal was to improve the efficiency of internal combustion engines, which has remained a primary benefit of turbocharging.
In the decades that followed, turbocharging technology saw limited application, primarily in aviation and racing. It wasn't until the 1970s that the automotive industry began to adopt turbochargers more widely, especially as manufacturers sought to meet new emissions standards and fuel economy regulations.
The advancement of materials technology and manufacturing processes has played a crucial role in the evolution of turbocharged engines. Modern turbos use lightweight, high-strength alloys that can withstand the extreme temperatures and pressures generated during operation.
Furthermore, the integration of turbocharging into everyday consumer vehicles became more prevalent in the 1990s, with companies like Volvo and Saab leading the charge. As consumer preferences shifted toward smaller, more fuel-efficient engines, turbocharging became a vital technology.
Today, turbocharging is no longer seen as a niche technology but as a standard feature in many vehicles, allowing manufacturers to deliver both power and efficiency, catering to a broader audience of environmentally conscious consumers.
How Turbocharging Works
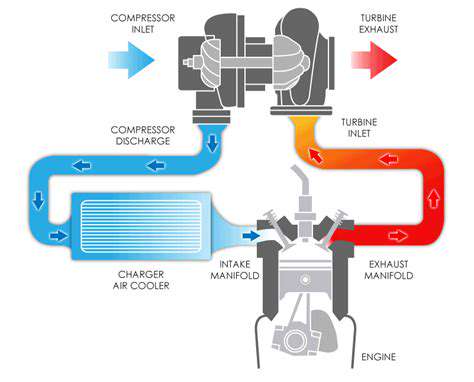
At its core, a turbocharger utilizes exhaust gas energy to compress incoming air, allowing the engine to draw in more air and fuel. This process significantly enhances the engine's power output without the need for increasing its size.
A typical turbocharger consists of two main components: the turbine and the compressor. The turbine is fed exhaust gases, causing it to spin rapidly, while the compressor drawing in ambient air is driven by the turbine's speed. This double action effectively boosts the engine's air intake.
Boost pressure is critical in this process. When the engine is under acceleration, the turbocharger's compressor can increase the intake pressure, allowing for more air and fuel to enter the combustion chamber, resulting in a more powerful explosion during the combustion cycle.
Turbo lag is a well-known phenomenon associated with turbocharged engines. This delay between pressing the accelerator and the turbocharger providing additional power can be attributed to the time it takes for the exhaust gases to spool up the turbine. However, advancements in turbocharger design, such as twin-scroll and variable geometry turbos, have helped mitigate this issue.
The effectiveness of turbocharging is directly influenced by factors such as engine size, fuel type, and operating conditions. From small displacement engines in compact cars to high-performance sports models, turbocharging remains a versatile solution in modern engine design.
The Advantages of Using Turbocharged Engines
Turbocharged engines are celebrated for their ability to deliver improved fuel economy without sacrificing performance. By forcing more air into the engine, turbochargers enable smaller engines to produce power levels comparable to larger, naturally aspirated engines.
One significant advantage of turbochargers is their ability to enhance power without a proportional increase in engine size or weight. This leads to lighter vehicles, which can improve handling and reduce wear on suspension components due to decreased mass.
Turbocharged engines also help reduce carbon emissions. By extracting more power from each unit of fuel, manufacturers can meet stringent regulations while delivering a performance that appeals to enthusiasts and eco-conscious drivers alike.
Another benefit is the flexibility in design. Turbocharging technology can be easily integrated into both gasoline and diesel engines, making it a versatile choice for vehicle manufacturers aiming to broaden their engine offerings.
Finally, turbocharged engines often provide a more responsive driving experience. When tuned correctly, these engines can deliver a surge of power that enhances acceleration and makes them enjoyable to drive in various conditions, from city traffic to open highways.
Challenges and Future of Turbocharged Engines
Despite their numerous benefits, turbocharged engines face several challenges. One major concern is the complexity associated with their design and maintenance. Turbo systems are intricate, and ensuring their longevity requires regular upkeep, such as timely oil changes and management of boost pressure.
Heat management is another significant issue. Turbochargers generate substantial heat, which can impact engine components if not managed accurately. Engineers continue to work on improving cooling systems and materials to handle the high temperatures associated with turbocharged engines.
Furthermore, there’s the challenge of turbo lag, which, while being diminished in modern systems, still presents a hurdle in delivering smooth power delivery. Manufacturers are investing in technology improvements to minimize this lag and enhance driver experiences.
Looking ahead, the future of turbocharging is likely tied to the overall shift toward hybrid and electric vehicles. Turbocharged engines can play a transitional role in providing a performance boost while manufacturers develop and refine their electrification strategies.
As regulations become more stringent around emissions and fuel efficiency, the ongoing innovation in turbocharging technology may pave the way for more sustainable engines that harness the best of both worlds: performance and environmental responsibility.
Benefits of Turbocharging: Efficiency and Performance

Understanding Turbocharging Technology
Turbocharging is a technology that uses exhaust gases to drive a turbine, which compresses incoming air. This process allows for a denser air-fuel mixture, leading to improved combustion efficiency. As a result, turbocharged engines can produce more power without significantly increasing fuel consumption.
Modern turbochargers are equipped with advanced features, such as variable geometry or twin-scroll designs, which optimize performance across a wider range of conditions. These innovations help eliminate turbo lag, enhancing the driving experience by delivering power more smoothly. Ultimately, this leads to better responsiveness and acceleration.
Additionally, turbocharging is not limited to high-performance vehicles; it is increasingly found in everyday cars to meet fuel efficiency standards. By allowing smaller engines to perform like larger ones, manufacturers can reduce vehicle weight while maintaining power output. This contributes to lower emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
Impact on Fuel Economy
The efficiency of turbocharged engines is largely attributed to their ability to extract more energy from the fuel consumed. By improving the combustion process, these engines can achieve significant gains in miles per gallon (MPG). This is particularly beneficial for drivers seeking cost-effective solutions without sacrificing performance.
Many turbocharged vehicles are designed to operate at optimal efficiency, even under varying load conditions. Smart technologies, such as direct fuel injection, complement the turbocharger by delivering fuel more precisely to match the engine's needs. This synergy enhances overall fuel economy, making these vehicles an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers.
The choice of turbocharged engines is not just a trend; it reflects a growing demand for vehicles that are both powerful and economical. Manufacturers are continually investing in research and development to improve the fuel-saving capabilities of turbocharged systems, ensuring that they remain competitive in the automotive market.
Performance Advantages Over Naturally Aspirated Engines
Turbocharged engines outperform their naturally aspirated counterparts by delivering higher power levels without a corresponding increase in engine size. This capability allows for more compact designs, which are particularly advantageous in smaller vehicles. Therefore, drivers can enjoy sporty performance while benefiting from a lightweight build.
Moreover, the enhanced torque provided by turbocharged engines is available at lower RPMs. This translates to better acceleration and responsiveness, making turbocharged vehicles more enjoyable to drive. The result is a more exciting driving experience, especially in scenarios that demand quick bursts of speed, such as merging and overtaking.
As automotive technology progresses, turbocharging is becoming more common across various vehicle classes. The versatility of this technology means that both sports cars and family sedans can harness the advantages of turbocharging, appealing to a broader range of consumers and their diverse needs.
Environmental Considerations
Turbocharged engines can contribute to reduced emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice. By maximizing fuel efficiency and enhancing performance, these engines produce fewer greenhouse gases compared to larger, naturally aspirated engines. This is an important factor as governments around the world enforce stricter emission regulations.
Additionally, turbocharging often leads to the development of vehicles that incorporate lightweight materials and innovative designs. These advancements in engineering not only improve performance but also align with sustainability goals by lowering resource consumption. As a result, turbocharged vehicles have become a preferred option for manufacturers looking to improve their green credentials.
It is worth noting that with the rise of hybrid and electric vehicles, turbocharged technology has also begun to play a role in the evolution of these systems. By integrating turbocharging into hybrid designs, engineers can achieve powerful and efficient vehicles that meet the demands of modern consumers while supporting environmental initiatives.
Future Developments in Turbocharging
The future of turbocharging is bright, with ongoing advancements aimed at enhancing both performance and efficiency. Engineers are exploring various materials and designs to reduce turbocharger weight and improve responsiveness further. These innovations are likely to lead to even more compact and powerful turbocharged engines.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and smart algorithms into engine management systems promises to optimize turbocharger performance dynamically. Such systems will analyze driving conditions in real-time and adjust the turbocharging process for optimal fuel efficiency and power delivery.
As electric powertrains continue to gain traction, manufacturers may also look to hybridize turbocharging with electric boosting technologies. This combination could offer drivers the instant torque associated with electric motors while benefiting from the traditional performance characteristics of turbocharged combustion engines, representing a significant leap forward in automotive technology.
Challenges and Solutions in Turbocharged Engine Design
Understanding Turbocharging Technology
Turbocharging technology is a method used to enhance an engine's performance by forcing more air into the combustion chamber.
By increasing the amount of air, turbocharged engines can burn more fuel, leading to improved power output.
This technology not only boosts horsepower but also can improve fuel efficiency when designed correctly.
Turbochargers utilize the engine's exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which in turn compresses the intake air.
This process allows smaller engines to perform like larger ones, demonstrating the efficiency and power potential of modern automotive engineering.
Common Challenges in Turbocharged Engine Development
One of the main challenges in turbocharged engine design is managing heat effectively.
Excessive heat can lead to engine knock and premature wear, which necessitates robust cooling systems.
Another challenge involves ensuring the reliability and durability of the turbocharger itself under varying operational conditions.
Engine responsiveness can also be a concern, as turbo lag may result in a delay from when the driver accelerates to when the engine produces power.
Manufacturers are constantly innovating to minimize these issues while maximizing performance and efficiency.
Solutions for Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
To combat heat issues, engineers are developing advanced materials and coatings that can withstand higher temperatures.
Additionally, implementing better cooling strategies, such as intercoolers, helps maintain optimal engine temperatures.
To address turbo lag, some manufacturers utilize twin-scroll turbos or variable geometry turbos, which improve response times.
Strategies such as adaptive engine management systems can help optimize performance based on driving conditions.
These innovations contribute not only to improved performance but also to the longevity and reliability of turbocharged engines.
The Future of Turbocharged Engine Technology
The automotive industry is seeing a trend towards downsizing engine sizes while still incorporating turbocharging for improved performance.
This approach not only meets regulations for emissions but also appeals to consumers seeking greater fuel economy.
Electric and hybrid vehicles are also integrating turbocharged engines to enhance efficiency without losing power.
This dual focus on performance and sustainability sets the stage for the future of turbocharged technologies.
Research into alternative fuels and turbocharged hybrid powertrains is a growing area of interest that could redefine how vehicles operate in the coming years.
The Future of Turbocharged Engines
The Evolution of Turbocharged Technology
Turbocharged engines have come a long way since their inception. Initially utilized in high-performance vehicles, technological advancements have allowed for their introduction in standard consumer cars. This shift has made turbocharging more accessible and appealing to a broader audience.
One of the key developments in turbocharging technology is the improvement in materials used for turbochargers. Modern turbines are made from lightweight, durable materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures, significantly enhancing their efficiency and longevity.
Another important milestone is the advent of electronic wastegate control. This technology allows for better management of boost levels, resulting in improved throttle response and smoother power delivery. As a result, drivers experience a more dynamic and engaging ride.
The integration of variable geometry turbos has also revolutionized the way turbochargers boost engine performance. By changing the geometry of the turbine at different RPMs, these sophisticated systems optimize airflow and improve efficiency across various driving conditions.
Fuel Efficiency Benefits
One of the most significant advantages of turbocharged engines is their ability to enhance fuel efficiency. By forcing more air into the combustion chamber, these engines can burn fuel more completely, resulting in better mileage without sacrificing power.
This efficiency is particularly important in today’s automotive landscape, where regulations on emissions and fuel consumption are becoming increasingly stringent. Turbocharged engines help manufacturers meet these standards while still delivering powerful performance.
Moreover, consumers benefit from lower fuel costs due to the enhanced efficiency of turbocharged vehicles. This aspect not only helps individuals save money but also contributes to a reduction in overall fuel consumption, which is beneficial for the environment.
The ability of turbocharged engines to deliver power without the need for larger displacement engines means that vehicles can maintain their performance while using smaller, more efficient powertrains. This trend will likely continue to gain momentum as consumers seek more sustainable options.
Performance Enhancements
Turbocharged engines are known for their ability to produce significantly more power than their naturally aspirated counterparts. This performance advantage is largely due to the increased amount of air being forced into the engine, which allows for more fuel to be burned.
Additionally, turbocharging minimizes the effects of engine lag by providing boost at lower RPMs. This means that drivers can experience an immediate response from the accelerator, enhancing the overall driving experience.
Many sports and high-performance vehicles have successfully implemented turbocharging to achieve their remarkable acceleration and top speeds. This technology has opened up new possibilities for engineers and designers to create vehicles that push the limits of performance.
As competition in the automotive market increases, manufacturers are continually looking for ways to differentiate their vehicles. Turbocharged engines provide an effective means of offering drivers a thrilling and powerful ride without compromising on fuel economy.
The Environmental Impact of Turbocharged Engines
As awareness of environmental issues grows, the automotive industry is actively seeking ways to reduce its carbon footprint. Turbocharged engines play a crucial role in this transition by providing a means to improve fuel efficiency and lower emissions.
Incorporating turbocharging technology can lead to a significant reduction in harmful exhaust emissions. By promoting a more complete combustion process, turbocharged engines often produce fewer greenhouse gases compared to traditional engines.
Furthermore, the smaller engine sizes often associated with turbocharging mean that vehicles can be lighter and more aerodynamic, which further contributes to fuel efficiency and reduced emissions.