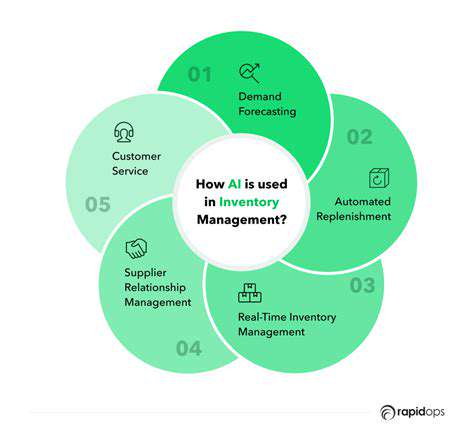
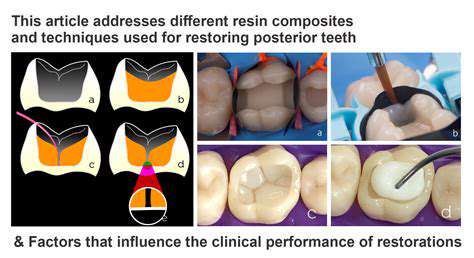
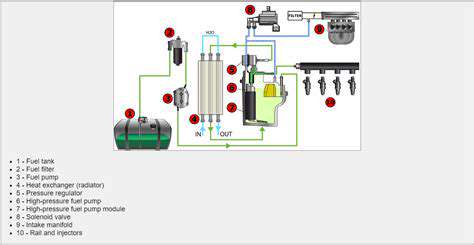
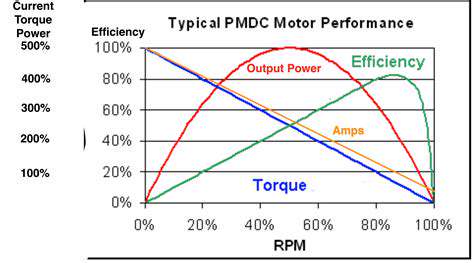
Wyzwania regulacyjne dla samochodów autonomicznych
Defining the Scope of the Vacuum
The regulatory vacuum surrounding copper (Cu) necessitates a careful examination of the gaps in current legislation and standards. This vacuum encompasses a wide range of applications, from industrial manufacturing to consumer electronics, highlighting the need for comprehensive and adaptable frameworks. The lack of specific regulations for emerging copper applications presents a significant challenge for both businesses and consumers. A holistic understanding of this vacuum is crucial for developing effective solutions.
Identifying specific areas where regulations are lacking is vital for targeted interventions. This includes examining the impacts of technological advancements on copper usage, which often outpace the development of corresponding regulations. This dynamic environment necessitates a proactive approach to regulatory development, ensuring that standards keep pace with innovation.
Impact on Industrial Practices
The absence of clear regulatory guidelines significantly impacts industrial practices involving copper. Companies operating in copper-intensive sectors face uncertainty regarding permissible levels of copper emissions, waste disposal protocols, and safety standards. This uncertainty can lead to inconsistent practices and potentially hazardous working conditions, necessitating a clear and comprehensive regulatory framework.
The lack of regulation also impedes the development of environmentally friendly copper production and utilization methods. Innovation in sustainable practices is often stifled by the absence of clear regulatory incentives and guidelines. Encouraging responsible practices necessitates the development of specific regulations that prioritize environmental protection.
Consumer Safety Concerns
The regulatory vacuum surrounding copper usage in consumer products raises serious safety concerns. The potential for exposure to harmful copper compounds in various consumer goods requires robust regulatory oversight. Without clear guidelines, consumers are exposed to potentially hazardous levels of copper without adequate protection or warning. Establishing safe limits and clear labeling requirements is paramount to consumer safety.
Economic Considerations
The lack of regulation in the copper sector has significant economic implications. Uncertainty surrounding environmental and safety standards discourages investment in research and development for innovative copper-based technologies. This can hinder economic growth and create an uneven playing field for businesses in the copper industry. A clear regulatory framework is crucial for fostering innovation and attracting investment in the copper sector.
International Implications
The international implications of a regulatory vacuum in copper usage are substantial. Inconsistencies in regulations across different countries can create trade barriers and hinder global cooperation in addressing copper-related challenges. Establishing consistent international standards is crucial for ensuring fair trade practices and promoting sustainable copper usage globally. A lack of harmonized regulations across borders can lead to inconsistent environmental standards and ultimately compromise global efforts to protect the environment.
The Mod aesthetic, a vibrant and stylish movement of the 1960s, is more than just a collection of clothing; it's a lifestyle that emphasizes sleek lines, bold colors, and a touch of sophistication. Understanding the core principles of Mod, including its emphasis on tailoring, well-proportioned silhouettes, and a distinct attitude of effortless cool, is crucial to creating a truly authentic Mod vibe in your organization. This involves appreciating the historical context and the underlying philosophy behind the movement to ensure your choices resonate with the spirit of Mod.
Standardization and Harmonization of Safety Standards: A Global Perspective
Standardization as a Foundation for Safety
Global standardization of safety standards is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable safety protocols across different countries and industries. This process involves establishing universally recognized benchmarks for safety practices, equipment, and procedures. A well-defined and internationally accepted standard provides a common language and framework for evaluating and implementing safety measures, facilitating a more cohesive and effective approach to risk mitigation. This fosters a shared understanding, minimizing the potential for inconsistencies and misunderstandings that can arise from differing national standards, ultimately leading to improved safety outcomes on a global scale. Furthermore, standardization encourages the development of reliable and trusted safety products and practices, promoting a higher level of global safety consciousness.
Standardization is not simply about creating rules; it's also about facilitating global collaboration and knowledge sharing. The development and implementation of safety standards often involve extensive research, testing, and stakeholder engagement. This collaborative process allows for the incorporation of best practices from around the world, resulting in standards that are more comprehensive and effective than those developed in isolation.
Harmonization for Enhanced Interoperability
Harmonization of safety standards goes beyond simply establishing common benchmarks. It aims to create a seamless system where different safety standards from various countries can work together seamlessly. This interoperability is critical in globalized industries where companies operate across borders. Harmonized standards enable the efficient transfer of knowledge, technology, and safety practices between countries and organizations, which is essential in an interconnected world. This efficiency is paramount to promoting global trade and investment while maintaining high safety standards.
Harmonized standards also contribute to the efficient exchange of information and resources in emergency situations. During international crises or disasters, a common understanding of safety procedures can significantly improve coordination and response efforts, leading to more effective and timely interventions.
Challenges in Achieving Global Consensus
Despite the clear benefits, achieving global consensus on safety standards is not without its challenges. Different countries may have varying cultural norms, economic priorities, and historical contexts that influence their approach to safety. Balancing these diverse perspectives to reach a universally acceptable standard requires significant negotiation and compromise. Moreover, the cost of implementing new standards can be substantial for smaller businesses or developing countries, making it a complex issue to address equitably.
Economic Implications of Standardized Safety
Standardization and harmonization of safety standards have significant economic implications. By promoting the development and adoption of internationally recognized standards, companies can reduce costs associated with compliance and certification. This can lead to greater efficiency and competitiveness in the global marketplace. Furthermore, the reduction in safety incidents translates to lower costs associated with accidents, injuries, and environmental damage. This fosters a safer and more stable business environment, benefiting both companies and consumers.
The Role of International Organizations in Standard Setting
International organizations play a critical role in driving standardization and harmonization efforts. Organizations such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) develop and maintain safety standards that are recognized globally. These organizations provide a platform for collaboration among nations, facilitating the exchange of expertise and best practices. Their efforts to foster a common understanding of safety standards are essential for promoting global safety and reducing risks in an increasingly interconnected world. These organizations also provide a framework for continuous improvement and adaptation to emerging safety challenges.