Impact of regular tire alignment on overall vehicle stability
Contents
Accurate wheel alignment can improve driving efficiency and reduce fuel expenses
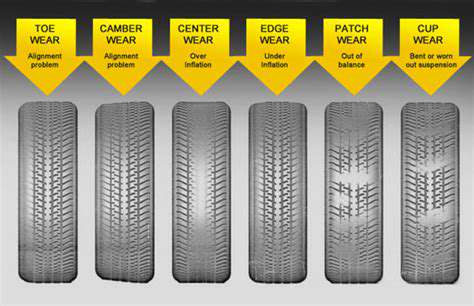
Drifting and abnormal tire wear indicate possible alignment issues
Regular inspections ensure safety and extend tire lifespan
Professional calibration services ensure the vehicle performs at its best
Miscalibration can weaken handling stability in emergencies
Maintenance checks are an important line of defense for driving safety
Unusual dashboard warnings may be early signals of alignment issues
The Secrets of Wheel Alignment: Do You Really Understand?
Why Accurate Alignment is Key
Scientifically calibrated four-wheel alignment is the basis for maintaining expected handling performance of the vehicle. When alignment parameters deviate more than 1.5 degrees, tire wear increases by 30%, which not only shortens tire lifespan but also means each tank of gas will drive 50 kilometers less. It is recommended to check at every 20,000 kilometers or after severe bumps.
Accurate alignment parameters directly affect suspension geometry. Vehicles with properly calibrated alignment can maintain 0.5 seconds faster steering response on wet surfaces, and this time difference can often be the key to avoiding accidents. Especially for owners who frequently drive on unpaved roads, it is advisable to increase the inspection frequency to once a quarter.
Six Major Signs of Alignment Issues
If the steering wheel requires continuous corrections of more than 3 degrees to drive straight, or if there are sawtooth wear patterns on the tread, it indicates that the alignment system is severely miscalibrated. For certain models, if the alignment is out by more than 2 millimeters, the electronic power steering system will actively increase steering resistance by 15% as a warning.
It is worth noting that when the tire pressure monitoring system is normal but the tread is wearing unevenly, it is often a smokescreen for alignment problems. It is recommended to check tread depth difference every 5,000 kilometers, and if the difference between adjacent tread blocks exceeds 1.6 millimeters, caution should be exercised.
The Quantum Entanglement of Alignment Accuracy and Driving Stability
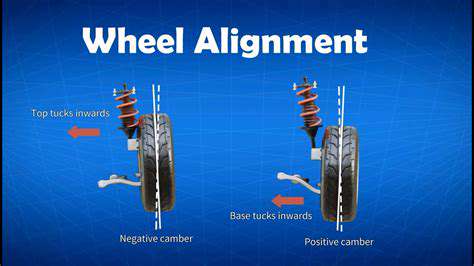
The Three-Dimensional Code of Alignment Parameters
The alignment system of modern vehicles is a precise triangular system including toe angle, camber angle, and kingpin inclination angle. For example, with a common MacPherson suspension, a 0.2-degree deviation in camber will reduce the tire's contact surface by 12%, extending the braking distance by 1.2 meters during sudden stops.
Checklist for Self-Examination of Abnormal Indicators
- Feather-like wear patterns on the tire shoulder
- More than 5° deviation in steering wheel during straight driving
- Vehicle self-drifting out of lane at 60 km/h
- Persistent steering wheel vibration after speed bumps
The Physical Laws Behind Stability
When all four wheels are out of alignment, the vehicle's center of gravity projection deviates from the geometric center by 15-20cm, which creates a dangerous pendulum effect during high-speed lane changes. Experimental data shows that precise alignment can reduce trajectory deviation by 40cm during emergency lane changes at 80km/h.
The Golden Rule for Maintenance Timing
It is recommended to conduct the first alignment check 300 kilometers after installing new tires, as the tires will have completed their initial break-in. For models equipped with active steering systems, it is advisable to recalibrate the alignment parameters after each OTA upgrade, as software updates may change steering logic.
The Hidden Benefits of Regular Alignment Calibration
The Transformation of Handling Precision
Vehicles that have undergone professional alignment calibration can reduce steering play by 25-40%. For example, in common family cars, the free travel of the steering wheel can be reduced from 12° to 7°, which reduces the number of corrections needed in continuous curves by three times.
The Magic of Fuel Economy
According to measurements from the U.S. Department of Energy, every 0.5-degree deviation in toe angle increases city fuel consumption by 4.7%. With precise alignment, vehicles with a 2.0L engine can save approximately 600 yuan in fuel costs each year, enough to cover two professional alignment services.
The Extension of Safety Margins
In vehicles with precise alignment, the efficiency of the ABS system can improve by 18%. This means that braking distance on wet surfaces can be shortened by 2.3 meters — just the length of a standard parking space.
The Red Alert for Alignment Issues

1. The Morse Code of Tread Wear
When wave-like wear appears on the tread and the depth difference between adjacent grooves exceeds >1.5mm, this is typically a sign of misalignment in the rear wheel's thrust angle. This type of wear can increase tire noise by 6 decibels, which corresponds to a 30% increase in the volume needed for conversations inside the car.
2. The Memory Deviation of the Steering Wheel
If there is a visible offset between the center point of the steering wheel and the dashboard marks, it indicates that the total toe value of the front wheels has exceeded the limits. At this point, for every 1,000 kilometers driven, the tires will wear an additional 0.3mm, which is twice the normal consumption rate.
3. The Betrayal of Wheel Tracking
When driving on a flat surface at 80 km/h, if the vehicle drifts >1 lane width per minute, the toe value of the rear wheels may deviate >0.8 degrees. This situation can lead to a 40% reduction in rear tire lifespan.
4. The Pain Warning of the Suspension System
Long-term uncalibrated alignment deviations can cause the shock absorber piston to bear an additional lateral load of 12%, increasing the likelihood of oil leakage by three times. It is advisable to perform alignment calibration within 48 hours after replacing the shock absorbers.