Safe practices for inspecting and replacing serpentine belts
Table of contents
Summaries*- The serpentine belt is a critical component of a vehicle's engine, powering essential accessories.
- Regular inspection and replacement of the serpentine belt are crucial for maintaining optimal vehicle performance.
- A serpentine belt's condition affects the performance and longevity of the engine's accessories.
- Inspecting the serpentine belt involves checking for wear, tension, and alignment.
- Replacing the serpentine belt requires proper tooling, safety measures, and following the correct routing diagram.
- Pre-inspection checklists and safety protocols are essential for a safe and efficient serpentine belt inspection or replacement.
- A comprehensive pre-inspection checklist includes verifying the vehicle's position, disconnecting the negative battery cable, and using personal protective equipment (PPE).
- A detailed inspection involves visually checking the belt's ribs, feeling its surface, and checking the belt tensioner's functionality.
- Replacing the serpentine belt requires following the correct routing diagram, using the proper tools, and re-tightening the tensioner.
- A safe serpentine belt replacement process involves gathering tools and safety measures, disconnecting the negative battery cable, and using PPE.
The Serpentine Belt: Your Engine's Unsung Hero
Safe Inspection Procedures

Pre-Inspection Checklist and Safety Protocols
Prior to initiating any inspection or replacement of a serpentine belt, a comprehensive pre-inspection checklist is absolutely essential to ensure a safe and efficient process. This should begin with verifying that the vehicle is parked on a level surface and the parking brake is firmly engaged, preventing any unexpected movement during the procedure. Next, a thorough examination of the immediate work area for potential hazards such as loose tools, slippery substances, or any other obstructions that could pose a risk to the technician’s safety is highly recommended, preventing falls and other injuries.
Furthermore, it is imperative to disconnect the negative battery cable before beginning any work on the engine’s belt system, as this minimizes the risk of electrical shocks, particularly during the removal and installation of components related to the belt drive. This safety step can prevent accidental shorts or system malfunctions. Moreover, the technician should always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses to protect against flying debris and gloves to maintain a firm grip on tools and prevent skin irritation from automotive fluids, and consider wearing hearing protection if the inspection is to be carried out with the engine running.
Additionally, always consult the vehicle’s service manual for the specific procedures, torque specifications, and belt routing diagrams relevant to the make and model of the vehicle. This is a fundamental step and helps prevent costly errors by ensuring that the correct belt type and routing are used, and that the tensioning system is properly adjusted after installation to the manufacturer's specifications, guaranteeing optimal performance and longevity of the replacement belt. Thorough preparation and adherence to the vehicle’s specific instructions are crucial for a safe and successful serpentine belt inspection or replacement, demonstrating professionalism and ensuring a quality outcome.
Detailed Inspection and Replacement Techniques
A thorough inspection of the serpentine belt involves several key steps that determine its condition and the need for replacement. Begin by visually inspecting the entire length of the belt for any signs of wear and tear, like cracks, glazing, or fraying, which often indicate a deteriorating belt and imminent failure; be sure to observe all sides of the belt, including the inner and outer surfaces, when inspecting. Pay close attention to the belt’s ribs; these are prone to damage, and any cracks or missing chunks indicate that the belt needs to be replaced immediately to prevent a potential breakdown, as well as prevent damage to other engine components.
To further assess the condition of the belt, feel its surface for any signs of unusual hardness or flexibility. A belt that feels unusually hard has likely lost its elasticity and is prone to slippage, which can lead to reduced performance of driven accessories, while a belt that feels extremely brittle can snap. Also, check the belt tensioner for proper functionality; ensuring the tensioner is operating correctly, the spring is not weak or broken, and the pulley rotates smoothly and without noise, as a faulty tensioner can cause premature belt failure, which can compromise the proper operation of the engine.
When replacing the serpentine belt, it's crucial to follow the correct routing diagram, which can often be found under the hood or in the vehicle’s service manual. The belt should be installed over all the pulleys in the correct order, taking note of any special instructions, like the direction of the belt's travel, as indicated by the arrows on the new belt. Using the correct tools, such as a serpentine belt tool or a wrench, carefully release the tension on the belt tensioner to remove and install the belt, ensuring the belt stays in place. Proper alignment of the new belt is crucial; carefully check the belt’s position on each pulley, and then re-tighten the tensioner and be prepared to run the engine briefly to verify the belt is operating correctly and is not emitting unusual noises.
Safe Serpentine Belt Replacement: A Step-by-Step Guide
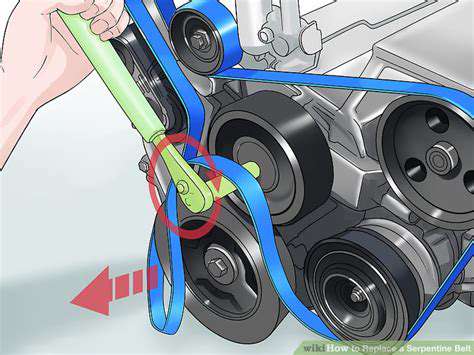
1. Preparation is Key: Gathering Tools and Safety Measures
Before you even think about touching your vehicle's serpentine belt, meticulously gather all the necessary tools and equipment to ensure a smooth and safe replacement process. This proactive approach minimizes potential delays and, more importantly, significantly reduces the risk of injury during the procedure, reinforcing the importance of careful planning and preparation within the realm of automotive maintenance. Be sure to have the correct size wrench or belt tensioner tool for your specific vehicle model; consult your owner’s manual or a reliable online resource to pinpoint the proper requirements, as utilizing the wrong tools can lead to stripping bolts, damaging components, and creating frustration.
Always prioritize safety by wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses to shield your eyes from debris and gloves to enhance your grip and protect your hands from sharp edges and any potential contamination. Ensure your vehicle is parked on a level surface, the parking brake is engaged, and the engine is completely cool before initiating any work. Disconnecting the negative battery cable is also a crucial step to prevent accidental starting of the engine and potential electrical shocks, guaranteeing your personal safety throughout the repair. Verify that your workspace is well-lit and free of any obstructions to allow easy maneuverability and prevent accidental trips or falls, promoting a clear and safe environment for your project.
Furthermore, having a high-quality serpentine belt replacement kit that matches your vehicle's specifications is essential, preventing a series of inconveniences. Check the kit's contents to confirm that it includes the correct belt, as well as any accompanying hardware or instructions; this preliminary verification guarantees you possess all the required components for the job at hand, thereby minimizing unforeseen setbacks. Consider documenting your vehicle's configuration with photographs or notes before removing the old belt, particularly regarding the routing path, as a visual reference can prove incredibly invaluable during the installation phase, helping to avoid costly errors.
Finally, consider using a creeper for ease of movement under the vehicle, especially if working in a confined space. Having a helper on hand can also be beneficial, particularly when tensioning the belt or maneuvering around tight areas, allowing for collaborative support and assistance; this collaborative approach enhances both the efficiency and the overall safety of the replacement process, providing an extra layer of support. Be sure to have a clean, organized workspace to prevent contamination of the belt or other components, further contributing to the project’s success.
2. Identifying and Inspecting the Existing Serpentine Belt
Once your workspace is prepared and you have assembled your tools, the next critical step is to accurately identify the location of your vehicle's serpentine belt and to conduct a thorough inspection of its current condition, evaluating wear and identifying potential issues. Typically, the serpentine belt snakes around the engine's various accessories, such as the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump, so familiarize yourself with these components and their typical locations under the hood. Consulting your vehicle's owner's manual or referencing online diagrams can provide precise information on the belt's exact location and its routing path, saving time and avoiding frustration.
Begin your inspection by carefully examining the entire length of the belt for visible signs of wear and damage, such as cracks, fraying, glazing, or missing ribs. Cracks indicate the belt's rubber is deteriorating and could lead to premature failure, while fraying suggests the belt is separating and losing its structural integrity. Glazing, which appears as a shiny, hardened surface, is often a sign of excessive heat or slippage, leading to reduced performance and potentially complete breakdown. Don't neglect to check for any signs of unusual noise or vibration, as these could be early indicators of a failing serpentine belt or problems with the associated pulleys or tensioner, highlighting the importance of detecting these anomalies.
Pay close attention to the ribs on the underside of the belt, as these are responsible for gripping the pulleys and transferring power. Examine the ribs for any signs of damage, such as missing chunks, wear patterns, or embedded debris. Also, check the belt's tension by gently pressing on it between two pulleys; if the belt deflects excessively, it may indicate the tensioner is failing or the belt is stretched beyond its operational limits, which might lead to performance issues. The inspection is not only about the belt itself, it's about the whole system.
If you discover any significant damage or if the belt shows signs of significant wear, such as deep cracks, glazing, or fraying, it is essential to replace it without delay. Even if the belt appears to be in good condition, consider replacing it at the recommended intervals, often every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, as part of a proactive maintenance schedule; this precautionary measure minimizes the risk of unexpected breakdowns and enhances the reliability of your vehicle. Thoroughly documenting all the components, along with pictures is a useful tactic for future reference.
3. Belt Removal: Releasing Tension and Taking it Out
With your vehicle inspected and prepared, you are now ready to remove the existing serpentine belt, initiating the process of safe replacement. The central challenge lies in releasing the tension from the belt tensioner, a spring-loaded mechanism that keeps the belt taut. Locate the tensioner, which is usually identifiable by its pulley and a lever arm, and you can find the tensioner by following the routing diagram. The vehicle’s service manual provides detailed instructions and the proper tool; using an incorrect tool is a critical source of safety hazards and vehicle damage.
Once the tensioner is identified, you must use the correct tool to release the tension on the belt. Typically, this involves a wrench, a belt tensioner tool, or a socket on the tensioner's pulley or arm. Insert the tool onto the tensioner and apply force in the direction indicated in your vehicle's manual or the diagram, usually counterclockwise or clockwise. Keep the tensioner held back while simultaneously removing the serpentine belt from one of the pulleys – this could be the smooth pulley or the grooved pulley, depending on the routing path, ensuring that you remove the belt carefully.
Once the belt is off, slowly release the tension on the tensioner, allowing it to return to its original position, and safely secure the tensioner tool in place. Note the precise routing path of the belt; many vehicles have a diagram of the belt routing under the hood, or you can take pictures of it. This diagram is crucial for installing the new belt correctly, and it can also save a lot of time. Incorrect routing of the belt can cause numerous problems, including engine overheating, accessory malfunctions, and even severe damage to the engine or accessories.
Before completely removing the old belt, carefully compare it with the new belt to ensure they are identical in length, width, and rib configuration. Any subtle difference in specification can result in improper fit, premature wear, or operational issues. After ensuring the new belt is compatible, remove the old belt, being mindful not to lose any components; this prevents the possibility of losing any parts during the process. Carefully store the old belt for future reference, and be prepared to show the belt to a professional for expert analysis to identify potential underlying issues.
4. Installing the New Serpentine Belt: A Precise Procedure
With the old serpentine belt removed and a new replacement ready, the installation process demands meticulous attention to detail to guarantee proper functionality. First, compare the new belt's routing to the diagram or your recorded reference, assuring that the belt goes around the pulleys in the correct order, as this is crucial. Carefully begin threading the new belt around the various pulleys, starting with the easiest accessible pulley. The belt should sit within the grooves of the pulleys with precision; if this condition isn’t met, it can lead to incorrect function and a series of problems.
Use the tensioner tool to release tension on the tensioner once the belt is partially in place, following the instructions from the removal step. Holding the tensioner back, carefully work the remaining portion of the belt onto the last pulley, being careful to avoid letting the belt slip off the other pulleys during this step. Confirm that the belt is properly seated in all the pulley grooves; if the belt is misaligned, it can damage the belt and the pulleys, which can ultimately lead to failure and cause potential danger. Make sure there is no interference.
Once the belt is in place, slowly release the tensioner tool, allowing the tensioner to apply the correct amount of tension to the belt. Double-check the belt's routing one final time to ensure that it is accurately positioned and aligned with all the pulleys, as a final quality assurance measure. The belt should be taut, but not excessively so; some deflection is normal. If the belt feels too tight, it may place undue stress on the components; too loose, and it will likely slip and fail to drive accessories properly.
After the belt is installed, start the engine and allow it to run for a few minutes while observing the belt's operation. Check for any unusual noises, vibrations, or belt slippage, which would indicate that the belt is not properly seated or the tensioner is not functioning correctly; correct these as soon as you can. Also, inspect the belt and all the components after a brief run, and then again after a longer test drive; this is a good way to confirm there aren’t any unexpected issues and that the job is well done.
5. Final Checks and Post-Replacement Considerations
With the new serpentine belt installed and operating smoothly, perform a final inspection and consider some important post-replacement steps to ensure optimal performance and long-term reliability. Carefully re-inspect the belt's routing, ensuring that it remains precisely aligned with all pulleys and that there are no signs of slippage or contact with any surrounding components, which can be dangerous. Listen for any unusual noises, such as squealing or chirping, and if these are present, investigate their source immediately, since these can be indicators of problems. Verify the operation of all the accessories driven by the serpentine belt, including the alternator, power steering pump, air conditioning compressor, and water pump, making sure they function as expected.
Take a short test drive to evaluate the vehicle's performance, and be attentive to any changes in engine behavior or accessory operation. Listen for any unusual sounds that could indicate problems with the new belt or associated components. During the initial driving period, observe the belt's condition periodically for any early signs of wear or misalignment; this early intervention helps to prevent a major breakdown. Consult your vehicle's owner’s manual for recommended maintenance schedules and torque specifications, as this will assist you in sustaining the vehicle’s components.
Keep the old serpentine belt for reference, and record the date and mileage of the replacement in your vehicle maintenance log, which could be critical. Documenting the replacement helps in tracking the belt's lifespan and ensuring that it is replaced at the recommended intervals, preventing premature failure. Consider consulting a professional mechanic if you experience any difficulties or if you are not comfortable performing any aspect of the replacement process. Your vehicle’s health is important; if you need help, make use of available resources.
Furthermore, consider replacing the belt tensioner and idler pulleys at the same time as the serpentine belt, especially if they show signs of wear or damage; these components contribute to the belt's proper function. Replace all the components as a preventative measure, as they can significantly increase the longevity and reliability of the entire system. Proactively replacing these components helps to avoid the added inconvenience of future failures and ensures the efficient operation of your vehicle's essential systems. This is a preventative approach that provides peace of mind.