Camshaft Position Sensor: Valve Timing
Introduction to the Camshaft Position Sensor

Understanding the Camshaft Position Sensor
The camshaft position sensor (CMP) is a crucial component in internal combustion engines, playing a vital role in accurately determining the position of the camshaft. This sensor, typically located near the camshaft itself, sends electrical signals to the engine control module (ECM) which provides critical information about the engine's operation. Understanding its function is essential for diagnosing and troubleshooting potential engine issues. Its precise measurements enable the ECM to control various engine functions, such as fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve actuation, ensuring optimal engine performance.
The CMP sensor's readings are translated into electrical signals that are fed into the ECM. This continuous feedback loop allows the ECM to precisely adjust engine functions in real-time, reacting to changes in engine speed and load conditions. This real-time monitoring is paramount to maintaining a smooth and efficient combustion process within the engine. A malfunctioning CMP sensor can lead to a cascade of issues, impacting overall engine performance and potentially causing significant problems.
Camshaft Position Sensor Function
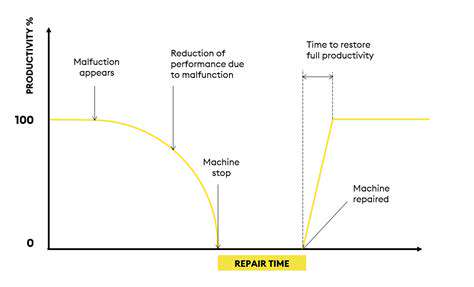
The primary function of the camshaft position sensor is to monitor the position of the camshaft within the engine. This is achieved through various methods, often utilizing magnetic or Hall effect technology. These technologies generate a specific electrical signal pattern that correlates directly with the camshaft's position. This data is crucial for the engine control module to regulate timing and ensure that the valves open and close at the correct moments in the combustion cycle. Accurate camshaft position data is essential for efficient fuel combustion and engine power output.
The sensor's output signal is a key input for the engine control module (ECM). The ECM utilizes this data to adjust various engine parameters, ensuring optimal performance and fuel economy. This includes precise control over fuel injection, ignition timing, and valve timing. These precise adjustments directly impact the overall engine efficiency and performance.
Troubleshooting Camshaft Position Sensor Issues
A malfunctioning camshaft position sensor can manifest in several ways, ranging from rough idling to complete engine failure. Diagnosing the problem often involves checking for codes stored in the engine control module. Checking the electrical connections and the physical integrity of the sensor itself is also crucial for accurate diagnosis. Visual inspection and testing are important steps to ensure the sensor is functioning correctly.
Beyond basic checks, more advanced diagnostic tools can assist in pinpointing the issue. These tools can help isolate the problem to the sensor itself, the wiring harness, or the ECM. Professional diagnostics may be needed to fully understand the scope of the problem and implement the necessary repairs. Identifying and addressing the problem promptly can prevent further damage to the engine and ensure a smoother operation. Incorrect operation of the sensor can result in costly repairs and downtime, so prompt investigation is key.
How the Camshaft Position Sensor Works
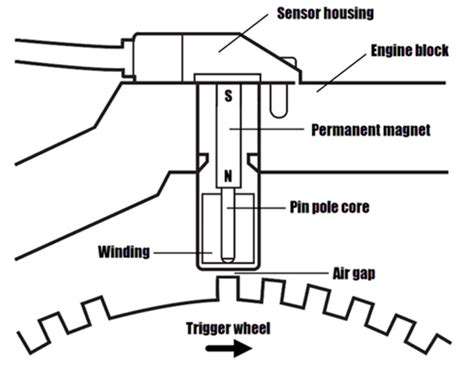
How Camshaft Position Sensors Work
Camshaft position sensors (CPS) are crucial components in internal combustion engines, playing a vital role in accurately determining the position of the camshaft. These sensors are responsible for providing crucial feedback to the engine control module (ECM), enabling it to manage ignition timing and fuel injection precisely. Understanding how these sensors function is key to appreciating their importance in modern engine management systems.
Types of Camshaft Position Sensors
Several types of CPS exist, each with its own design and operating principles. Some common varieties include magnetic and Hall-effect sensors. Magnetic sensors often utilize a magnetic field generated by the camshaft to detect its position, while Hall-effect sensors rely on the principle of the Hall effect to sense the magnetic field variations. Understanding the differences between these types is essential to troubleshooting issues.
Electrical Principles
The electrical signals generated by CPS are vital for engine operation. These signals are typically analog and represent the camshaft's position. The specifics of the signal waveform and voltage levels are crucial for accurate interpretation by the ECM. These signals are directly related to the precise operation of the engine. The electrical circuitry surrounding the sensor is also important for proper operation.
Signal Processing and Interpretation
The ECM receives the electrical signals from the CPS and processes them to interpret the camshaft's position. Complex algorithms within the ECM interpret these signals, providing precise data for engine management. This data plays a critical role in determining the proper timing for fuel injection and ignition. Accurate signal processing is paramount for efficient engine performance.
Relationship to Engine Control Module (ECM)
The ECM relies heavily on the information provided by the CPS to control various engine functions. The ECM uses the data to coordinate ignition timing, fuel injection, and other critical processes. Maintaining a stable and accurate connection between the sensor and the ECM is essential for engine performance. Malfunctioning or inaccurate signals can lead to significant engine performance issues.
Troubleshooting and Diagnosis
Diagnosing problems with a CPS often involves testing the sensor's output signal. Using specialized diagnostic tools, technicians can identify issues like faulty wiring, open circuits, or sensor malfunctions. These issues can result in various engine problems, from misfiring to rough idling. Proper troubleshooting is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective repairs.
Maintenance and Replacement
Regular maintenance of CPS, including checking for corrosion and damage, is recommended. Replacing a faulty CPS is often necessary to restore optimal engine performance. Symptoms of a failing CPS can include rough idling, misfiring, and loss of power. Identifying and addressing these issues promptly can prevent more significant engine problems.