Understanding the benefits of high capacity radiators for trucks
Addressing the Challenges of Harsh Environments
Extreme Temperatures: A Major Concern
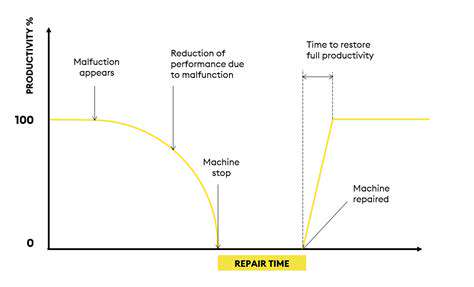
Harsh environments often present extreme temperature fluctuations, posing significant challenges to equipment and personnel. Sustained exposure to intense heat can lead to equipment malfunctions, reduced efficiency, and potential safety hazards for workers. Conversely, extreme cold can cause equipment to freeze, making it inoperable, and also poses significant risks to human health, requiring specialized protective gear and procedures.
The design and maintenance of equipment must consider these temperature extremes. Materials need to be selected for their ability to withstand the range of temperatures, and regular maintenance schedules must account for the potentially accelerated degradation caused by these conditions. Proper insulation and cooling systems are crucial in mitigating the effects of extreme temperatures.
Exposure to Corrosive Chemicals
Many harsh environments are characterized by the presence of corrosive chemicals, which can rapidly degrade equipment and pose serious health risks to personnel. These chemicals can react with metals, causing pitting, corrosion, and structural weakening. This poses a significant threat to the integrity and longevity of equipment, requiring careful material selection and robust protective coatings.
Regular inspections and proactive maintenance are essential to identify and address corrosion issues early on. Implementing strict safety protocols and providing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for workers are crucial for mitigating the health risks associated with exposure to corrosive chemicals.
Inadequate Infrastructure and Logistics
Harsh environments often lack the robust infrastructure necessary for reliable operations. This includes issues such as limited access roads, unreliable power grids, and a scarcity of water resources. These logistical challenges can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of operations, necessitating careful planning and contingency measures.
Developing alternative solutions for power generation, water supply, and transportation is crucial in overcoming the limitations of inadequate infrastructure. This may involve implementing backup power systems, establishing water purification processes, or developing specialized transportation methods.
Dust and Debris Accumulation
High levels of dust and debris accumulation can significantly impact the performance and lifespan of equipment in harsh environments. Dust and debris can clog machinery, reduce airflow, and cause friction, leading to accelerated wear and tear. This necessitates regular cleaning and maintenance procedures to prevent these issues.
Specialized equipment and techniques may be needed to effectively manage dust and debris. Consideration should be given to the use of high-pressure air systems, specialized filters, and regular cleaning schedules to maintain optimal equipment function.
Seismic Activity and Natural Disasters
In geographically challenging areas, seismic activity and the threat of natural disasters such as floods, earthquakes, or landslides pose significant risks to operations. Equipment must be designed and anchored to withstand these potential events. Emergency response plans should be in place to minimize the impact of such events.
Extreme Weather Conditions
Beyond temperature extremes, harsh environments can experience intense winds, heavy rainfall, or extreme snowfall. These conditions can significantly impact the operation of equipment and the safety of personnel. Robust design and construction are essential to withstand the forces of wind and rain, with appropriate drainage systems and protective measures in place.
Understanding the specific weather patterns of the environment is critical for planning and implementing effective safety measures. This includes incorporating weather forecasting data into operational procedures and developing contingency plans for extreme weather events.
Personnel Safety and Training
The safety of personnel working in harsh environments is paramount. Comprehensive training programs are crucial to equip workers with the knowledge and skills needed to handle the unique challenges of these environments. This includes training on hazard recognition, emergency procedures, and the use of personal protective equipment (PPE).
Regular safety assessments and incident reviews can help identify areas for improvement and ensure that safety protocols are continuously updated to address new risks. Creating a culture of safety, encouraging reporting of near misses and incidents, and fostering open communication about safety concerns are also vital for minimizing risks.