HTML
CSS
Electronic Power Steering (EPS)
Diagnostic Tools
Styling
電子パワーステアリング修理:現代ステアリング
概要
診断ツールと手順
EPSシステム診断の必須ツール
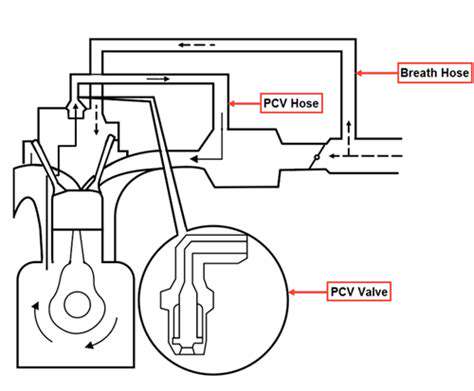
電動パワーステアリング(EPS)の故障に対処する場合、整備士は専用の診断機器に頼ります。現代のガレージでは、高度なスキャナーを使用して、
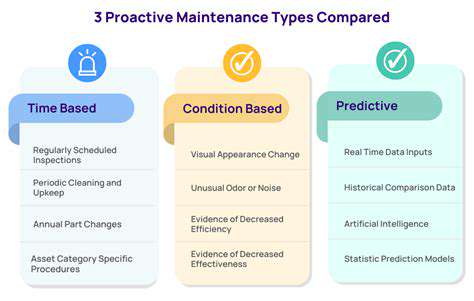
高度なEPSシステムのトラブルシューティングと保守

EPSシステムアーキテクチャの基礎
効果的なトラブルシューティングは、3つの主要なEPSアーキテクチャを理解することから始まります。
Read more about 電子パワーステアリング修理:現代ステアリング
多層防錆アプローチで、家屋を自然災害から保護します。外装防錆は住宅メンテナンスの重要な側面であり、腐食の悪影響から資産を守ります。この多層アプローチ...
Apr 30, 2025