Diagnosing and repairing common car AC compressor issues
Identifying Common Car AC Compressor Problems

Identifying the AC Compressor
The AC compressor plays a vital role in your vehicle's climate control system. This mechanical pump circulates refrigerant through the system, enabling the cooling process. Locating this component and understanding its basic operation forms the foundation for effective AC troubleshooting. Typical signs of compressor issues include unusual grinding noises, visible refrigerant leaks, or physical damage to the unit.
Finding the compressor requires some mechanical knowledge since it's usually mounted near the engine. Most compressors feature a cylindrical shape with refrigerant lines and electrical connections. Taking time to study your vehicle's specific layout can prevent misdiagnosis of AC problems.
Warning Signs of Compressor Failure
When an AC compressor begins failing, several noticeable symptoms emerge. You might experience reduced cooling efficiency, strange metallic grinding sounds, or intermittent cold air output. These warning signs typically intensify as the compressor's condition deteriorates, making early detection crucial.
Another red flag is increased engine temperature during AC operation. The struggling compressor creates additional load on the engine, potentially leading to overheating. Ignoring these symptoms may result in complete system failure and more expensive repairs.
Diagnostic Procedures
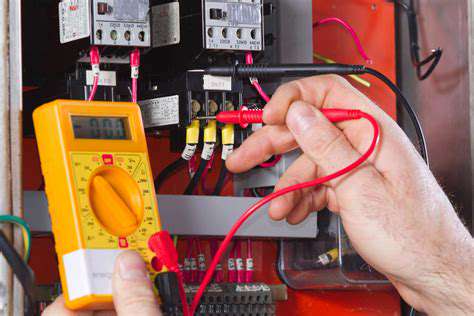
Begin troubleshooting with a thorough visual examination. Check for oil stains around fittings, inspect the drive belt for wear, and listen for abnormal noises during operation. Verifying refrigerant charge levels represents a critical step, as insufficient refrigerant can mimic compressor problems.
Electrical testing comes next. Examine wiring connections for corrosion and use a multimeter to check clutch operation. Proper voltage testing helps distinguish between electrical issues and mechanical compressor failures.
Replacement Cost Considerations
Compressor replacement expenses vary widely based on vehicle specifications. Labor charges often constitute the majority of repair costs, particularly for vehicles requiring special procedures. Component prices range from affordable aftermarket options to premium OEM parts.
Obtaining multiple professional estimates proves wise. Comparing different shops' recommendations and pricing structures leads to better informed financial decisions.
Alternative Repair Options
Before committing to full compressor replacement, explore other possibilities. Sometimes a simple refrigerant recharge or minor seal replacement solves the issue. Targeting the actual problem rather than automatically replacing components can yield significant savings.
Professional Assistance Benefits
DIY compressor repairs often create additional complications without proper training. Incorrect procedures may damage other AC components or create safety hazards. Certified technicians possess the specialized tools and knowledge for proper diagnosis. Expert service ensures correct repairs and helps prevent future system failures.
Refrigerant Leaks and Low Charge
Refrigerant Leak Issues
Refrigerant leaks represent one of the most frequent causes of AC performance decline. These leaks can develop at numerous system points including hose connections, service valves, and compressor seals. Locating the precise leak source proves essential for effective, lasting repairs. Gradual refrigerant loss leads to diminished cooling capacity and potential compressor damage if left unaddressed. Routine system inspections help detect leaks early, preventing major component failures.
Leak severity ranges from minor seepage to catastrophic failure. Small leaks might take months to noticeably affect performance, while major leaks cause immediate cooling loss. Understanding leak characteristics helps technicians determine appropriate repair strategies.
Low Charge Consequences
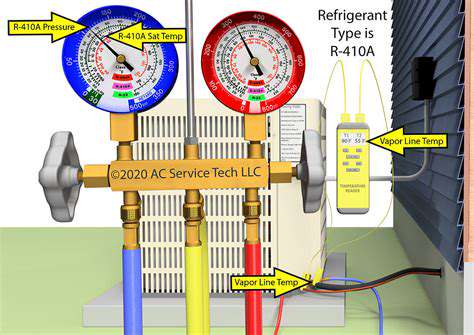
Inadequate refrigerant levels severely impact system operation. Without sufficient refrigerant, the AC system cannot properly absorb and transfer heat, resulting in poor cooling performance. The refrigeration cycle depends on precise refrigerant quantities - too little causes the compressor to work harder while delivering less cooling.
Common low charge indicators include longer cooling cycles, reduced vent temperatures, and compressor short-cycling. Prompt attention to these symptoms prevents accelerated component wear and system damage. Proper refrigerant charging requires specific equipment and training to ensure correct amounts.
Diagnostic Approaches
Effective leak detection combines multiple methods. Visual inspections reveal oily residue at leak points, while electronic detectors identify refrigerant traces. Advanced techniques like ultraviolet dye testing provide definitive leak location. System pressure measurements and temperature readings help assess overall refrigerant charge status.
After identifying issues, proper repair procedures must follow. This may involve component replacement, system evacuation, and precise refrigerant recharge. Quality repairs combined with preventive maintenance maximize system lifespan and efficiency.
Preventive Maintenance
Regular maintenance prevents most refrigerant-related problems. Scheduled inspections should examine all potential leak points and verify proper charge levels. This proactive approach catches minor issues before they become major repairs.
Proper refrigerant handling procedures ensure safety and environmental compliance. Following manufacturer specifications for refrigerant types and quantities maintains optimal system performance. Technicians must use proper recovery equipment and follow EPA guidelines during all servicing.