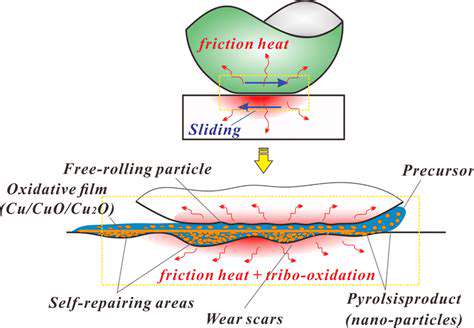
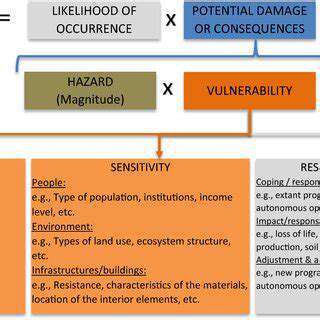
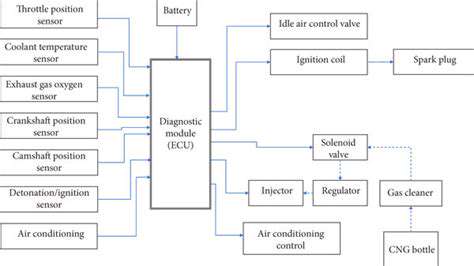
The role of thermal management in high performance vehicles
The Future of Thermal Management: Innovation and Efficiency
Emerging Technologies in Thermal Management
Modern thermal management is undergoing a transformation as electronic devices become more powerful yet smaller in size. Cutting-edge cooling methods like microchannel heat sinks and phase-change materials are emerging to tackle the growing heat dissipation challenges. These solutions aim to maintain optimal performance in increasingly compact systems by efficiently managing thermal output.
Material science breakthroughs are particularly exciting, with researchers developing advanced composites and nanostructured materials that conduct heat exceptionally well. These innovations could enable future devices to handle significantly higher power densities while maintaining stable operating temperatures.
Impact on Various Industries
The ripple effects of improved thermal management will be felt across multiple sectors. For consumer electronics, better heat control means we'll see more powerful smartphones, laptops, and AI systems that don't throttle performance or overheat. This advancement directly translates to longer battery life and more reliable operation for all our portable devices.
In transportation, particularly for electric vehicles, enhanced thermal regulation systems will lead to batteries that last longer and charge faster. Automakers can design more efficient cooling systems that improve both vehicle range and overall energy efficiency, pushing the boundaries of sustainable transportation.
Sustainability and Environmental Considerations
With growing environmental awareness, the thermal management field faces increasing pressure to develop eco-friendly solutions. Scientists are actively working on cooling technologies that use less energy and incorporate sustainable materials. This includes investigating natural refrigerants and passive cooling methods that reduce electricity consumption.
The industry must balance technological progress with environmental responsibility. Next-generation thermal solutions need to deliver high performance while minimizing ecological impact through smarter design and cleaner operation.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite promising developments, several hurdles remain before these technologies reach mainstream adoption. Manufacturing costs need reduction, and new systems must integrate seamlessly with existing designs. Engineers face the complex task of making advanced thermal solutions both affordable and practical for mass production.
Looking ahead, the focus should be on creating sophisticated modeling tools that can predict thermal behavior accurately. Such tools would allow for optimized designs that maximize cooling efficiency while minimizing energy use, paving the way for smarter thermal management across all applications.