How advanced filtration systems improve car air quality
HEPA Filters: Unmatched Particle Capture
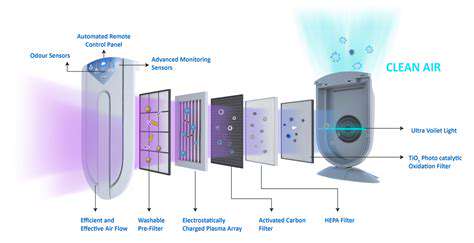
HEPA filters represent the gold standard in particulate filtration. Their multi-layered fiber matrix creates an impenetrable web that captures 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. This includes not just common allergens like pollen and pet dander, but also microscopic threats like bacteria and some viruses. What makes these filters truly remarkable is their ability to maintain this efficiency throughout their lifespan when properly maintained. For asthma sufferers and allergy-prone individuals, HEPA filtration isn't just beneficial - it's often life-changing.
Activated Carbon: The Molecular Sponge
While many associate activated carbon with odor elimination, its capabilities run much deeper. Each gram of this treated material contains surface areas equivalent to a football field, creating countless bonding sites for gaseous molecules. This unique property allows it to trap everything from formaldehyde emissions to toxic fumes from household cleaners. Unlike simple air fresheners that mask smells, activated carbon permanently removes the offending compounds. In urban environments where VOC levels frequently exceed safe limits, these filters provide critical protection against long-term chemical exposure.
The Dynamic Duo: Combined Filtration
Pairing HEPA and activated carbon creates a comprehensive defense system against airborne threats. While HEPA tackles particulate matter, the carbon component neutralizes gaseous pollutants that would otherwise pass straight through. This synergy proves particularly valuable in spaces like basements or urban apartments where mold spores and chemical vapors coexist. Modern hybrid systems now integrate these technologies so seamlessly that many users forget they're breathing filtered air - until they step outside and notice the difference.
Cutting-Edge Filtration Technologies
The filtration revolution extends far beyond traditional methods. Photocatalytic oxidation breaks down pollutants at the molecular level, while bipolar ionization creates charged particles that cause contaminants to cluster for easier capture. Some systems now incorporate real-time air quality monitoring that automatically adjusts filtration intensity based on pollutant levels. These innovations don't replace HEPA and carbon filtration, but rather enhance their effectiveness against emerging airborne threats.
Maintenance: The Key to Performance
A high-end filtration system only performs as well as its maintenance schedule. HEPA filters typically require replacement every 12-18 months, while activated carbon beds lose effectiveness after 3-6 months in polluted environments. Neglecting these changes essentially turns filters into pollutant reservoirs, potentially worsening air quality. Smart systems now track usage and alert users when replacements are due, taking the guesswork out of maintenance. Regular vacuuming of pre-filters can extend the lifespan of primary filters by up to 30%.
The Evolution of Vehicle Air Purification
Next-Generation Filtration
Automotive air purification is undergoing a quantum leap in sophistication. Future systems won't just filter air - they'll actively analyze and neutralize threats. Imagine filters that adapt their porosity based on particulate concentration, or carbon beds that regenerate themselves during nighttime charging. Some prototypes even incorporate nanotechnology membranes capable of capturing viruses with near-100% efficiency. These advancements promise to make vehicle cabins cleaner than many hospital environments.
Smart System Integration
The cars of tomorrow will treat air quality with the same importance as engine performance. Integrated sensors will continuously monitor cabin air composition, automatically adjusting filtration based on GPS location (entering a tunnel) or external conditions (forest fire smoke). Climate control systems will work in concert with purifiers, creating optimized airflow patterns that ensure no dead zones where pollutants accumulate. Some luxury models already feature air quality history logs accessible via smartphone apps - soon this may become standard across all vehicle classes.
Personalized Breathing Zones
Future systems will move beyond one-size-fits-all solutions to offer individualized air management. Through biometric sensors in seats and steering wheels, systems could detect when a driver's respiration rate indicates allergen exposure and automatically increase filtration. Parents might program child mode to provide extra protection against airborne pathogens. Some concepts even explore scent customization, allowing drivers to subtly infuse the cabin with invigorating or relaxing aromas based on time of day or driving conditions.
The Investment Perspective on Cabin Air Quality

The Volatility of Trend Investing
Market trends often resemble weather patterns - exciting to watch but dangerous to chase. The same psychological forces that create housing bubbles can distort valuations in emerging sectors like advanced filtration technology. Investors drawn to hot air quality stocks should remember that even legitimate innovations can become overvalued when excitement outpaces fundamentals. The key lies in distinguishing between fleeting hype and sustainable technological advantages.
Risk Assessment Essentials
Three critical questions every investor should ask: Does the company hold defensible patents or merely license technology? Is their revenue diversified or dependent on a single automaker partnership? Most importantly - does their solution address a genuine need or an imagined one? The air quality sector has seen countless breakthroughs that failed to transition from lab to marketplace. Successful investing here requires both technical understanding and cold-eyed business analysis.
Strategic Investment Approaches
Diversification proves particularly valuable in this sector. Rather than betting on single companies, consider ETFs that track clean air technologies. Pay attention to regulatory trends - upcoming emissions standards often create tailwinds for filtration innovators. Perhaps most crucially, maintain realistic time horizons; even the best air quality solutions typically take 5-7 years to achieve widespread automotive adoption. Patient investors who understand these dynamics can potentially profit from the coming clean air revolution without falling victim to its volatility.